Contact
Research interests - Statistics, data analysis, spatio-temporal modeling, spatial point processes, epidemiological models, mechanistic-statistical modeling, outbreak reconstruction from genomic data, pathogen spread, particle dispersal, exposure-hazard models, pathogen emergence
Research position Since 2017: Director of research from the Plant Health and Environment (SPE) department of INRAE, located in the BioSP research unit at Avignon, France Earlier positions and education
Management and administrative roles Since 2021: Deputy head of the Plant Health and Environment (SPE) department Since 2021: Member of the pilot committee of the French platform for epidemiosurveillance in plant health (Plateforme ESV) Earlier roles
Packages, web tools, and scripts tropolink: A webapp to explore air-mass trajectories and the geographic connectivities they generate (wiki) MoWPP: Model of Within-host Pathogen Population dynamics SLAFEEL: Statistical Learning Approach For Estimating Epidemiological Links from deep sequencing data COVID-19 Forecast: Real-time Covid19-mortality forecast at the country/state/province resolution RainfallFeedbackMaps: Maps to explore where rainfall feedback could be occurring briskaR: Biological risk assessment with R GMCPIC: Testing of the equality of vectors of probabilities (also available in StrainRanking) StrainRanking: Ranking of pathogen strains FeedbackTS: Analysis of feedback in time series CloNcaSe: Estimation of sex rate and effective size Anisotropic dispersal: Script for parameter estimation and sample design BIOBAYES: Scripts associated with the eponymous book
Lannou et al. (2023) - Editions QUAE The issue of health crises caused by invasive pests is essential in agriculture. This book deals with various questions on the subject, including: How do invasions occur? How do they spread? Why are they so frequent? What detection and identification tools are available to track these populations and trace their origins? Which models allow to analyze the risk, to predict it and to optimize the monitoring accordingly? Finally, how is society organized in the face of these crises?
Main projects IRIS (OFB, 2024-2026) PAPEETE (OFB, 2024-2026) BeXyl (EU, 2022-2026) BCOMING (EU, 2022-2026) BEYOND (ANR, 2021-2026) SEPIM (France Relance, 2021-2024) IPM Popillia (EU, 2020-2024) SMITID (ANR, 2016-2020; PI) RESISTE (ANR, 2019-2025) BriskaR-NTL (EFSA, 2018-2020) SPREE (ANR, 2017-2020) XF-ACTORS (EU, 2016-2020) AMIGA (EU, 2011-2016) PlantFoodSec (EU, 2011-2016) EMILE (ANR, 2009-2013; WP coord.) Group Dispersal (SPE, 2010-2012; PI)
ModStatSAP network - funded by the SPE, MathNum and SA departments of INRAE - Modeling and statistics for animal and crop health
PhD students Bartholomé Vieille (main supervisor) Ismaël Houillon Maria Choufany (main supervisor) Maryam Alamil (main supervisor) Candy Abboud (main supervisor) Coralie Picard Loup Rimbaud Vera Georgescu
Postdocs César Martinez Mélina Ribaud Virgile Baudrot Emily Walker Melen Leclerc Vincent Garetta David Pleydell Constance Xhaard
Postmasters Mathilde Thiébaud Dorian Chauvin | Hot topic: the BEYOND Project - ANR grant (2021-2026) in the Cultiver et protéger autrement PPR call. BEYOND: Building Epidemiological surveillance and prophYlaxis with Observations both Near and Distant; PI: Cindy Morris; co-PI: Samuel Soubeyrand. Many open positions will be available along the project, from master internships to postdocs, in multiple fields and multi-displinary domains of life science, statistics, data science and economics.
Hot topic: the SEPIM Project - FranceAgriMer grant (2021-2024) in the PNRI call Vers des solutions opérationnelles contre la jaunisse de la betterave sucrière. SEPIM: Surveillance, Évaluation, Prévision, Interpolation et Mitigation des risques relatifs à la jaunisse de la betterave; PI: Samuel Soubeyrand.
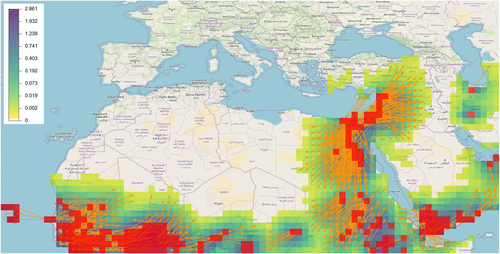
Richard et al. (2023) - GeoHealth - As air masses move within the troposphere, they transport a multitude of components including gases and particles such as pollen and microorganisms. These movements generate atmospheric highways that connect geographic areas at distant, local, and global scales that particles can ride depending on their aerodynamic properties and their reaction to environmental conditions. In this article we present an approach and an accompanying web application called tropolink for measuring the extent to which distant locations are potentially connected by air-mass movement... https://doi.org/10.1029/2023GH000885
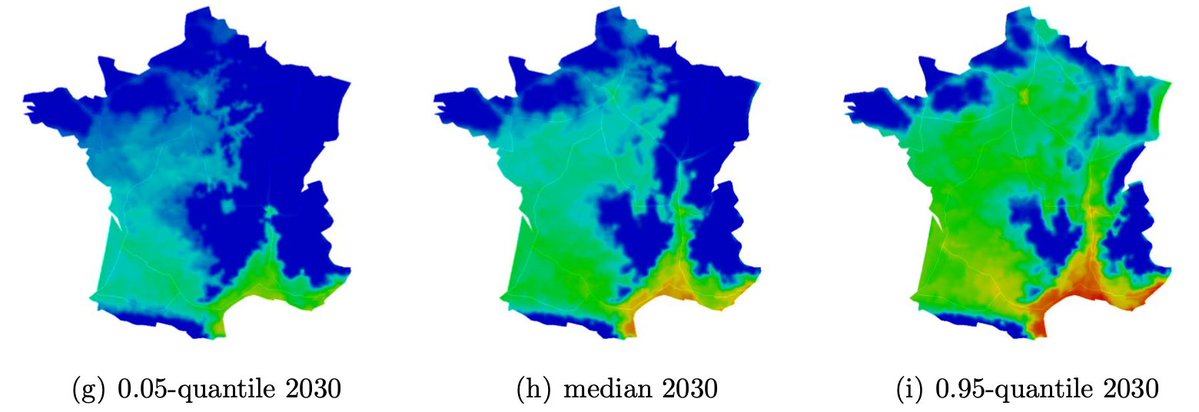
Roques et al. (2023) - Biological Invasions - France has a latitudinal range for the expansion of Aedes albopictus invasive populations that is not yet completely colonized providing a critical opportunity to address key invasion processes. We propose a spatio-temporal model (DISTIGRI) to describe and predict current and future expansions at intra- and inter-annual scales of A. albopictus... doi:10.1007/s10530-023-03062-y
Alamil et al. (2020) - Frontiers in Microbiology - High-throughput sequencing has opened the route for a deep assessment of within-host genetic diversity that can be used, e.g., to characterize microbial communities and to infer transmission links in infectious disease outbreaks. The performance of such characterizations and inferences [...] are often grounded on computer-intensive evaluations. Then, being able to simulate within-host genetic diversity across time under various demo-genetic assumptions is paramount to assess the performance of the approaches of interest. In this context, we built an original model that can be simulated to investigate the temporal evolution of genotypes and their frequencies under various demo-genetic assumptions... doi:10.3389/fmicb.2022.983938
Soubeyrand et al. (2020) - PLoS ONE - Discrepancies in population structures, decision making, health systems and numerous other factors result in various COVID-19-mortality dynamics at country scale [...]. Mortality dynamics of countries that are ahead of time implicitly include these factors and can be used as real-life competing predicting models. We precisely propose such a data-driven approach implemented in a publicly available web app timely providing mortality curves comparisons and real-time short-term forecasts... doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0238410
Baudrot et al. (2020) - Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety - Field cultivation of Genetically Modified (GM) Bt-plants has a potential environmental risk toward non-target Lepidoptera (NTLs) larvae through the consumption of Bt-maize pollen. The Bt-maize Cry protein targeting Lepidoptera species detrimental to the crop is also expressed in pollen which is dispersed by wind and can thus reach habitats of NTLs. To better assess the current ecological risk of Bt-maize at landscape scales, we developed a spatially-explicit exposure-hazard model... doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111215
Martinetti and Soubeyrand (2019) - Phytopathology - Recent detections of Xylella fastidiosa in Corsica Island, France, has raised concerns on its possible spread to mainland France and the rest of the Mediterranean Basin. [...] We present a new methodological approach for the design of risk-based surveillance strategies... doi:10.1094/PHYTO-07-18-0237-FI
SMITID project (2016-2020) - ANR grant ANR-16-CE35-0006 - Statistical Methods for Inferring Transmissions of Infectious Diseases from deep sequencing data
Mrkvicka and Soubeyrand (2017) - Spatial Statistics - Nowadays, spatial inhomogeneity and clustering are two important features frequently observed in point patterns. These features often reveal heterogeneity of processes/factors involved in the point pattern formation and interaction determining the relative locations of points. [...] In this article, we consider cluster point processes with double inhomogeneity... doi:10.1016/j.spasta.2017.03.005
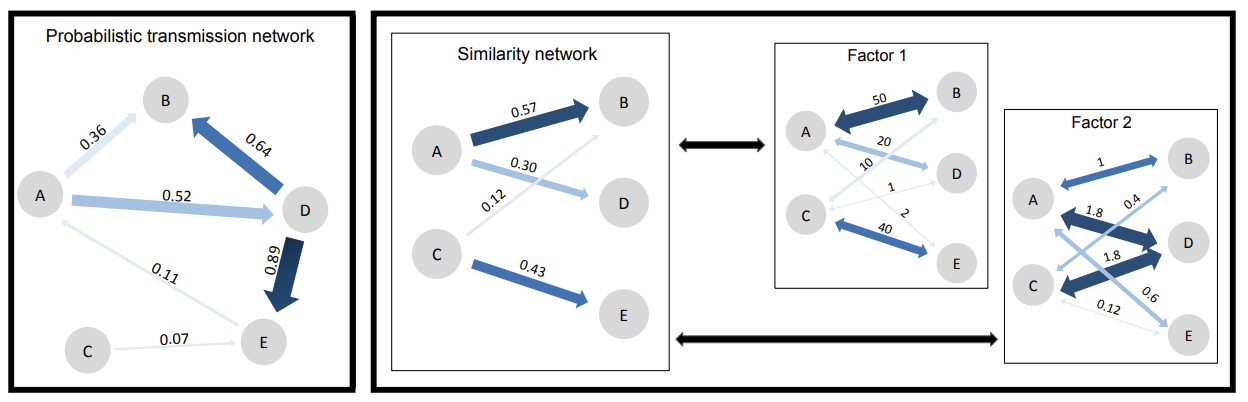
Soubeyrand (2016) - Journal de la SFdS - Identifying transmission links of an infectious disease through a host population is critical to understanding its epidemiology and informing measures for its control. To infer more reliably who-transmitted-to-whom [...], we present [an approach] that combines (i) an individual-based, spatial, semi-Markov SEIR model for the spatio-temporal dynamics of the pathogen, and (ii) a Markovian evolutionary model for the temporal evolution of genetic sequences of the pathogen... http://journal-sfds.fr/article/view/524
Mrkvicka et al. (2016) - Spatial Statistics - This paper reviews recent advances made in testing in spatial statistics and discussed at the Spatial Statistics conference in Avignon 2015. The rank and directional quantile envelope tests are discussed and practical rules for their use are provided... doi:10.1016/j.spasta.2016.04.005
Soubeyrand and Haon-Lasportes (2015) - Statistics and Probability Letters - The weak convergence of posterior distributions conditional on maximum pseudo-likelihood estimates (MPLE) is studied and exploited to justify the use of MPLE as summary statistics in approximate Bayesian computation (ABC). Our study could be generalized by replacing the pseudo-likelihood by other estimating functions (e.g. quasi-likelihoods and contrasts)... doi:10.1016/j.spl.2015.08.003
Mollentze et al. (2014) - Proceedings of the Royal Society B - We describe a statistical framework for reconstructing the sequence of transmission events between observed cases of an endemic infectious disease using genetic, temporal and spatial information... doi:10.1098/rspb.2013.3251
Soubeyrand et al. (2014) - Environmental Modelling & Software - Identifying and characterizing feedbacks in environmental processes may help in improving predictions for some environmental systems. The statistical study of time series is a manner to approach these feedbacks... doi:10.1016/j.envsoft.2014.07.003
| Full publication list - Click here
COVID-19 - "Data" blog maintained by members of BioSP
Xylella fastidiosa - Analyses and tools members of BioSP contributed to
Ribaud et al. (2023) - Statistics in Medicine - Classical supervised methods like linear regression and decision trees are not completely adapted for identifying impacting factors on a response variable corresponding to zero-inflated proportion data (ZIPD) that are dependent, continuous and bounded. In this article we propose a within-block permutation-based methodology to identify factors (discrete or continuous) that are significantly correlated with ZIPD... https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.9814
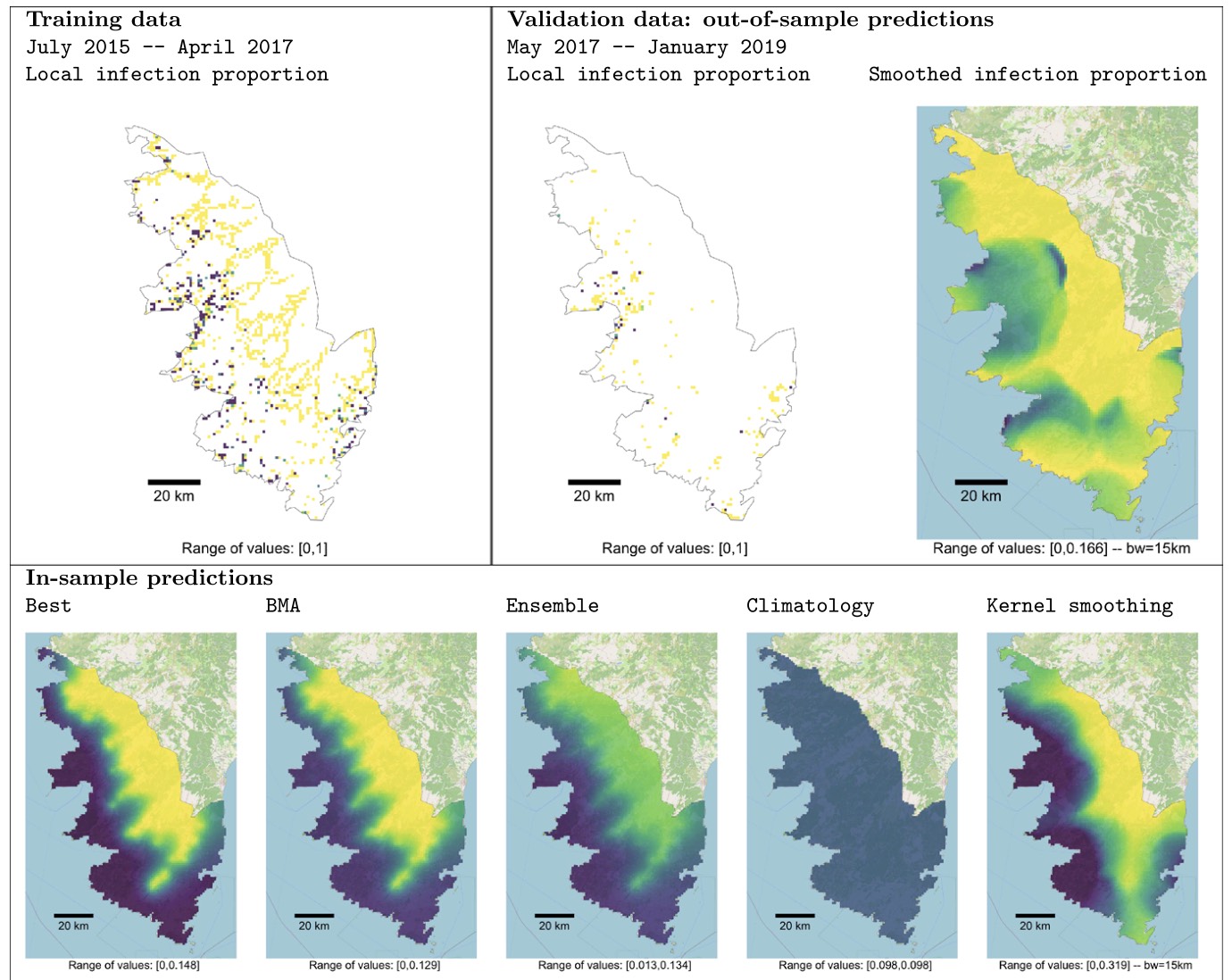
Abboud et al. (2023) - Bulletin of Mathematical Biology - Forecasting invasive-pathogen dynamics is paramount to anticipate eradication and containment strategies. [...] To avoid drawing a forecast grounded on a single PDE-based model that would be prone to errors, we propose to apply Bayesian model averaging (BMA), which allows us to account for both parameter and model uncertainties. [...] This approach is applied to predict the extent of Xylella fastidiosa in South Corsica... https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-023-01169-w
Eck et al. (2022) - The American Naturalist - The inherently variable nature of epidemics renders predictions of when and where infection is expected to occur challenging. Differences in pathogen strain composition, diversity, fitness, and spatial distribution are generally ignored in epidemiological modeling and are rarely studied in natural populations, yet they may be important drivers of epidemic trajectories... doi:10.1086/717179
Choufany et al. (2021) - Frontiers in Applied Mathematics and Statistics - The movement of atmospheric air masses [...] can be locally simplified by means of three-dimensional trajectories. These trajectories can hence be seen as a way of connecting distant areas [...]. In this paper we present a mathematical formalism to construct spatial and spatiotemporal networks [...] inferred from sampled trajectories of air masses [...] with potential implications in aerobiology and plant epidemiology... doi:10.3389/fams.2020.602621
Dvorak et al. (2019) - Spatial Statistics - For point patterns observed in natura, spatial heterogeneity is more the rule than the exception [...]. We propose parametric and semiparametric models of non-stationary LGCPs where the non-stationarity is included in both the mean function and the covariance function of the GRF... doi:10.1111/risa.12941
Walker et al. (2019) - Risk Analysis - We developed a simulation model for quantifying the spatio‐temporal distribution of contaminants (e.g., xenobiotics) and assessing the risk of exposed populations at the landscape level. The model is a spatio‐temporal exposure‐hazard model based on... doi:10.1111/risa.12941 See also the R package briskaR (Biological Risk Assessment with R)
Alamil et al. (2019) - Philosophical Transactions B - Here, we propose a statistical learning approach for estimating epidemiological links from deep sequencing data (called SLAFEEL), which is based on a parsimonious semiparametric pseudo-evolutionary model... doi:10.1098/rstb.2018.0258
Abboud et al. (2019) - Journal of Mathematical Biology - In this article, we are specifically interested in dating and localizing the introduction that led to an invasion using mathematical modeling, post-introduction data and an adequate statistical inference procedure. We adopt a mechanistic-statistical approach grounded on a coupled reaction–diffusion–absorption model representing the dynamics of an organism in an heterogeneous domain [...]. This framework is applied to the invasion of Xylella fastidiosa, a phytopathogenic bacterium detected in South Corsica in 2015, France... doi:10.1007/s00285-019-01376-x
BriskaR-NTL project (2018-2020) - EFSA grant OC/EFSA/GMO/2018/01 - Development of a spatially and temporally explicit model to quantify risks to non-target Lepidoptera
Soubeyrand et al. (2018) - New Phytologist - Unravelling the ecological structure of emerging plant pathogens persisting in multi‐host systems is challenging. In such systems, observations are often heterogeneous [...]. We designed a mechanistic‐statistical approach to help understand the ecology of emerging pathogens [...]. We applied our approach to French surveillance data on Xylella fastidiosa [...]. Xylella fastidiosa was probably introduced into Corsica much earlier than its discovery... doi:10.1111/nph.15177
Leyronas et al. (2018) - Frontiers in Microbiology - Many phytopathogenic fungi are disseminated as spores via the atmosphere from short to long distances. The distance of dissemination determines the extent to which plant diseases can spread and novel genotypes of pathogens can invade new territories. [...] The objective of the present study was to determine the interconnectivity of reservoirs of S. sclerotiorum from distant regions based on networks of air mass movement... doi:10.3389/fmicb.2018.02257
Picard et al. (2017) - Annual Review of Phytopathology - During the past decade, knowledge of pathogen life history has greatly benefited from the advent and development of molecular epidemiology. [...] Here, we review molecular epidemiology approaches that have been developed to trace plant virus dispersal in landscapes... doi:10.1146/annurev-phyto-080516-035616
Morelli et al. (2012) - PLoS Computational Biology - The accurate identification of the route of transmission taken by an infectious agent through a host population is critical to understanding its epidemiology and informing measures for its control [...]. We present here a framework leading to a Bayesian inference scheme that combines genetic and epidemiological data, able to reconstruct most likely transmission patterns and infection dates... doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002768
Soubeyrand et al. (2009) - The American Naturalist - The ecological and evolutionary dynamics of species are influenced by spatiotemporal variation in population size. Unfortunately, we are usually limited in our ability to investigate the numerical dynamics of natural populations across large spatial scales and over long periods of time. Here we combine mechanistic and statistical approaches to reconstruct continuous‐time infection dynamics of an obligate fungal pathogen... doi:10.1086/603624
Soubeyrand et al. (2008) - Journal of the Royal Statistical Society C - A spatiotemporal model is developed to analyse epidemics of airborne plant diseases which are spread by spores [...]. Maximum likelihood combined with a parametric bootstrap is proposed to estimate model parameters... doi:10.1111/j.1467-9876.2007.00612.x |